Click on the blue word above to pay attention to "vitality and harmony"


recent days
Issued by China CDC in official website.
No.795, Week 10, 2024
China Influenza Surveillance Weekly
↓ ↓ ↓
Summary of influenza epidemic situation in China
(As of March 10th, 2024)
Monitoring data show that the positive rate of influenza virus detection in southern and northern provinces continued to decline this week. B(Victoria) strain was the main strain, followed by A(H3N2) subtype and A(H1N1)pdm09 subtype. Twenty-two outbreaks of influenza were reported nationwide.
From April 3, 2023 to March 10, 2024 (based on the experimental date), 1875 strains (97.3%) of influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 virus were similar strains of A/Victoria/4897/2022; 1233 strains (40.9%) of influenza virus subtype A(H3N2) are similar strains of A/Darwin/9/2021 (chicken embryo strain); 1219 strains (40.4%) were similar to A/Darwin/6/2021 (cell strain); B(Victoria) strain 1052 (98.7%) is similar to B/Austria/1359417/2021.
Since April 3, 2023, drug resistance monitoring showed that all influenza strains of subtype A(H1N1)pdm09 were sensitive to neuraminidase inhibitors, except five strains of subtype A(H1N1)pdm09. All strains of influenza A(H3N2) and influenza B are sensitive to neuraminidase inhibitors. All influenza strains A(H1N1)pdm09, A(H3N2) subtype and B are sensitive to polymerase inhibitors.
Epidemic situation of novel coronavirus infection in China
(February 2024)
First, the report of severe infections and deaths in Covid-19.
From February 1 to February 29, 2024, 31 provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the Central Government) and Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps reported 358 new cases of severe illness and 22 deaths (including 0 cases of respiratory failure caused by Covid-19 infection and 22 cases of death caused by Covid-19 infection). See figure 1.
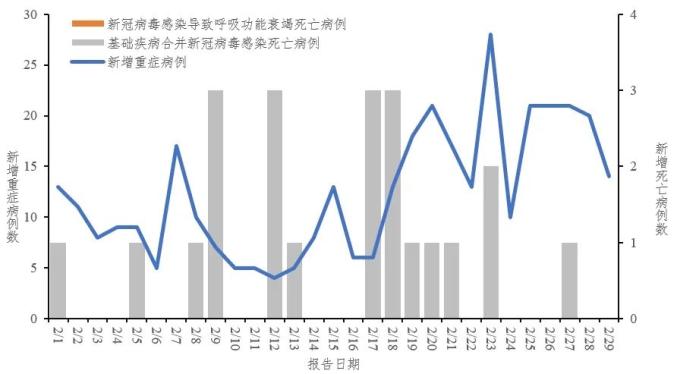
Fig. 1 Report of new severe and fatal cases of infection in Covid-19.
Two, the national fever clinic (clinic) diagnosis and treatment.
From February 1 to February 29, 2024, the number of fever clinics (consultation rooms) in 31 provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the Central Government) and Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps dropped from 202,000 on February 1 to 116,000 on February 9 (the lowest in this month), and then fluctuated and fell to the highest of 211,000 on February 19, and reached 158,000 on February 29. See figure 2.
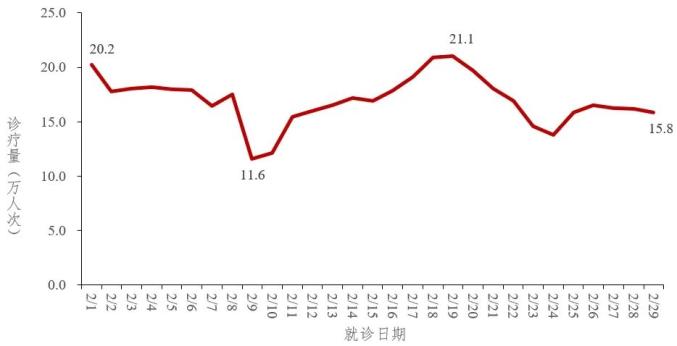
Fig. 2 The changing trend of the number of fever clinics (consulting rooms) in China.
Third, the sentinel hospital monitoring situation
From the fifth week (January 29-February 4) to the ninth week (February 26-March 3) in 2024, the proportion of influenza-like cases in outpatient (emergency) clinics in sentinel hospitals in China showed a trend of first rising and then falling, with the proportion of influenza-like cases being 6.1%, 6.7%, 6.8%, 5.4% and 5.0% respectively. See figure 3-1.
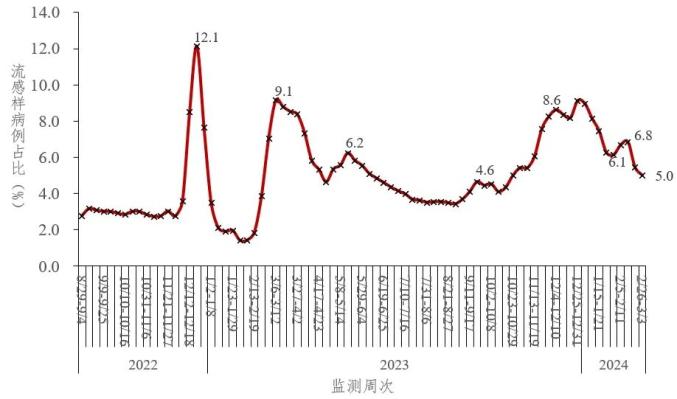
Figure 3-1 Changing trend of influenza-like cases reported by sentinel hospitals in China
The Covid-19 positive rate of influenza-like cases increased from 3.3% in the fifth week (January 29th-February 4th) to 14.3% in the ninth week (February 26th-March 3rd) in 2024. See figure 3-2.
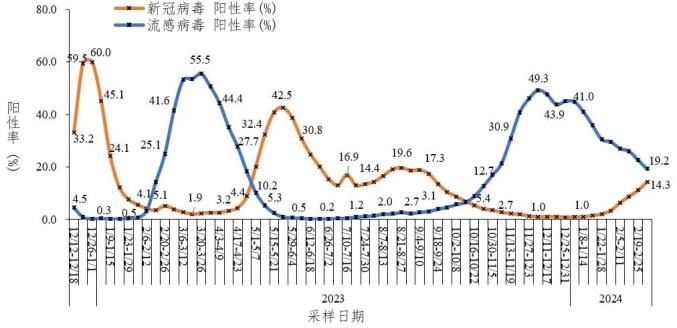
Figure 3-2 Trends of COVID-19 and Influenza Virus Positive Rate of Influenza-like Cases in National Sentinel Hospitals
IV. Monitoring of virus variation in local cases
From February 1 to February 29, 2024, 6653 local cases of Covid-19 genome were reported from 31 provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the Central Government) and Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps, all of which were Omicron variants, and the main epidemic strains were JN.1 series variants. According to the sampling date, the proportion of XBB and its sub-branches has been declining recently, while the proportion of JN.1 and its sub-branches has been increasing. See figure 4.
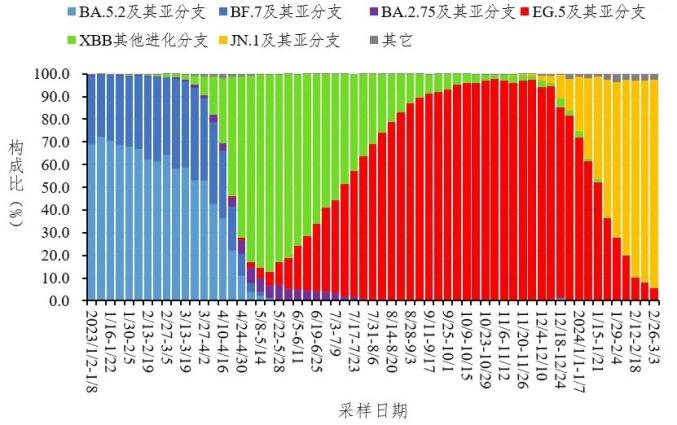
Fig. 4 Variation trend of local cases infected in novel coronavirus in China.
spring
It is the season of high incidence of respiratory infectious diseases.
It’s the turn of winter and spring.
Repeated climate change
In addition, there are more population movements.
In places where people are relatively concentrated
It is easy to cause the spread of respiratory infectious diseases
Please take good health protection.

Source/Pentium Rong Media
Editor/Jay Song Zhang Xiaomin
Audit/Wang Yuanfei
Final review/Ho Lee
News hotline/0474-7215507
Submission email/xhrmt2019@126.com
Disclaimer: Original manuscript of Xinghe County Rong Media
Please indicate that it is from the official WeChat of Vitality Xinghe.
Selected previous issues
"Xinghe News" See more publicity activities on the policy of "booking new recruits to join the army" in Xinghe County See more new times and new Lei Feng | Learn from Lei Feng and do practical things for the people in all parts of Wulanchabu City See more [Concern] Inner Mongolia vigorously promotes sand control and wind power photovoltaic integration project to see more safety production | Please don’t take the elevator when encountering these signs! read more
Original title: "Health science | involving influenza, COVID-19, the latest notification of Chinese disease control is coming …"
Read the original text